40 hcl molecular orbital diagram
How are the 3p orbitals of chlorine lower in energy than the 1s orbital of hydrogen? MO diagram of HCl. Share. Share a link to this question. Copy link1 answer · Top answer: I'd say there are two important things to consider here: Firstly, Cl is more electronegative than H. And secondly, as you proceed from the left to the ... Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
3-Dimensional representation of the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO). The LUMO is an anti-bonding orbital consisting of a Cl p-orbital and H s-orbital ...
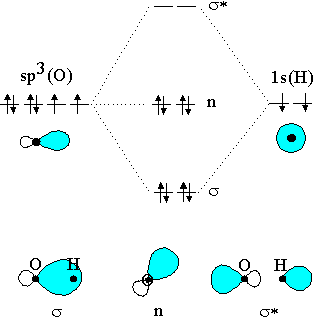
Hcl molecular orbital diagram
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. [1] [2] [3] A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the ... Here is a useful MO diagram of HCL found on the internet: The Cl electrons residing up to 3s orbital (1s, 2s, 2px,2py,2pz,3s) are largely stabilized than H electron in 1s orbital and therefore they cannot mix and form bond. The 3p electrons of Cl have comparable energy with the H electron and therefore are allowed to mix. Molecular Weight: in chemistry of a substance (sometimes called the molecular weight of a substance) is the mass of a molecule of that substance, relative to a unit of atomic mass (u which equals 1/12 of the mass of an n-carbon-12 atom) (simply: molecular mass is the sum of the weights atoms in a molecule). Molecular mass can be calculated as ...
Hcl molecular orbital diagram. The other sp2 hybrid orbitals form sigma bonds between C and H, therefore, leading to C-H single bonding structure. C2H4 Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram. The molecular orbital theory is a concept of quantum mechanics where atomic linearly combines to form molecular orbitals and we describe the wave nature of atomic particles. Molecular Orbital Diagram. HBr is a heterogeneous diatomic molecule. The molecular orbital theory is based on the chemical bonding concept of molecules. It is one of the most descriptive and diagrammatic representations of bonding where we deal with orbitals and energy levels inside a molecule. Tunneling from the HOMO-1 weakens the bond and, in the laser field, leads to fragmentation of the molecular ion. Hence, the breakup of an HCl molecule after ionization is a direct signature for tunneling from a lower-lying orbital. Fig. 1 ( A) Schematic diagram for the tunnel ionization and subsequent bond-softening processes of HCl in an ... Molecular Orbital Diagram - Cl2, Br2, I2 3s & 3p and higher atomic orbitals are not so widely separated in energy and allow significant mixing (hybridization) to occur. This mixing causes the inversion of the σσand πmolecular orbitals' energy. σσσ ππ σ* π* 3,4,5 p 3, 4,5 s σ* σ 3,4,5 s 3,4,5 p Interhalogens Br Br F F Br F F F F.
3 Jan 2021 — Just as with atomic orbitals, we create an energy-level diagram by listing the molecular orbitals in order of increasing energy. Chlorine is sp3-hybridized, and so there are four tetrahedrally-arranged 3sp3 orbitals surrounding it.Hydrogen does not hybridize, so it's simply a circle fo... ... here is the MO diagram for HCl: 1b1 and 1b2 are nonbonding because the 3px and 3py atomic orbitals of chlorine weren't compatible with hydrogen's 1s, and the 1a1 is nonbonding because the 3s of chlorine is too low in energy to interact with hydrogen's 1s. 2a1 and 3a1 are the σz and σ* z bonding and antibonding MOs, respectively. Cyanide Molecular Orbital Diagram Molecular orbital theory is also able to explain the presence of Figure \ (\ PageIndex {6}\): Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagram for HCl. to describe the bonding in the cyanide ion (CN −). mix atomic orbitals on different atoms to get Molecular Orbitals. The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this.
Purpose: Obtain molecular orbital results for total electronic energies, dipole moments, and bond orders for HCl, H 2, NaH, O2, NO, and O 3. The computationally derived bond orders are correlated with the qualitative molecular orbital diagram and the bond order obtained using the NO bond force constant. Introduction to Spartan/Q-Chem 20 Aug 2015 · 2 answersHere is a useful MO diagram of HCL found on the internet: The Cl electrons residing up to 3s orbital (1s, 2s, 2px,2py,2pz,3s) are largely stabilized than H ...What is the molecular orbital diagram of HCl and how ...1 answer11 Dec 2017What is the electronic configuration of an HCL molecule ...1 answer24 Dec 2017What is the Mot configuration of HCL? - Quora1 answer29 Apr 2021How can orbitals of H and Cl molecule combine to form ...1 answer29 Jun 2021More results from www.quora.com A qualitative molecular orbital diagram for ferrocene (D 5d) p p x e 1u z y a dyz dxz e 1g. Ferrocene Synthesis • Cyclopentadiene (b.p. 42.5 °C) is produced by cracking dicyclopentadiene (b.p. ... HCl solution and 5 g of ice in a 30‐mL beaker. • Collect the crude product by filtration on a Hirsh funnel. Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the energetically-favored configuration.
What is the molecular orbital diagram of HCl and how? Here is a useful MO diagram of HCL found on the internet: The Cl electrons residing up to 3s orbital (1s, 2s, 2px,2py,2pz,3s) are largely stabilized than H electron in 1s orbital and therefore they cannot mix and form bond.
The molecular orbital diagram of NH3 is presented in Figure 5 and will be elaborated in regards to its interactions. The s orbitals for the 3 hydrogens are used to set up the sigma and anti bonding combinations of N sp 3 orbitals and the H 1s orbitals. Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the ...
Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. Using quantum mechanics, the behavior of an electron in a molecule is still described by a wave function, Ψ, analogous to the behavior in an atom.Just like electrons around isolated atoms, electrons around atoms in ...
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
MO Diagram of HCl : In case of MO diagram of HCl, combination between the hydrogen 1s AO and chlorine 1s, 2s,2p and 3s orbital can be ruled out because their energies are too low. If the overlap occur between the chlorine 3p y and 3p z orbitals it would be non bonding because the positive lobe of hydrogen will overlap equally with positive and ...
Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of molecular orbital (MO) energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked by constituent atomic orbital (AO) energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels increasing from the bottom to the top. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels.
We're going to need the total number of bands electrons for hcl to fill out the molecular orbital energy diagram. So let's find this first.1 answer · Top answer: First, identify the number of valence electrons. The number of valence electron per element is based on the group number. [readmore]Next, fill the molecular ...
This lecture clearly explains the molecular orbital diagram of heteronuclear diatomic molecule (HF & HCl). This will help students of H.S., BS-MS, B. Sc., M....
Hydrogen chloride. Hydrogen chloride is a diatomic molecule. Carbon monoxide, CO, has a total of 10 valence electrons. To satisfy the octet rule for the carbon, the two atoms form a triple bond with six shared electrons in three bonding molecular orbitals. Since four of the shared electrons come from the oxygen atom and only two from carbon ...
Similarly, in the second and fourth option we can see the negative overlap where positive spin and negative spin containing orbitals are overlapping with each other.So HCl look like. Note: Always remember that positive overlap will be the result of two similar spins and negative overlap is always shown by two opposite spins. Also, the orbital ...
Molecular Orbital Diagrams. Let's consider two of the strong acids: HCl and HNO3. HCl is a molecule with only 2 atoms so we'll use the full molecular ...
Draw the Molecular Orbital Diagram for Hcl. Question 162. Essay . Draw the molecular orbital diagram for HCl.Use the valence shell electrons for each atom.What is the bond order? Explore answers and all related questions . Related questions. Q 163 . Explain the phenomenon of light absorption and emission from molecules.
molecules. The orbitals that combine will be those that are closest in energy. The closer in energy they are the stronger the stabilization of the bonding orbitals will be, and the stronger the bond. For example in HCl, the H 1s orbital is closest in energy to the Cl 2p orbital. Thus the orbital diagram is as follows.
Molecular Weight: in chemistry of a substance (sometimes called the molecular weight of a substance) is the mass of a molecule of that substance, relative to a unit of atomic mass (u which equals 1/12 of the mass of an n-carbon-12 atom) (simply: molecular mass is the sum of the weights atoms in a molecule). Molecular mass can be calculated as ...
Here is a useful MO diagram of HCL found on the internet: The Cl electrons residing up to 3s orbital (1s, 2s, 2px,2py,2pz,3s) are largely stabilized than H electron in 1s orbital and therefore they cannot mix and form bond. The 3p electrons of Cl have comparable energy with the H electron and therefore are allowed to mix.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. [1] [2] [3] A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the ...
Comments
Post a Comment