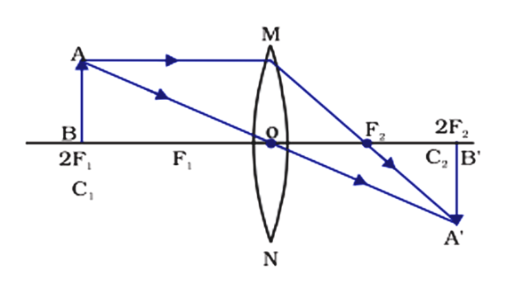
42 ray diagram for converging lens
PDF Chapter-9.pmd | 9.5.3 Power of a lens FIGURE 9.5 Ray diagram for image formation by a concave mirror. curvature of a concave mirror or appearing to pass through it for a. Wearing spectacles of converging lenses (used for near vision) will amount to more converging power than needed for parallel rays. Ray diagrams and images - Lenses - Edexcel - GCSE Physics... Learn about and revise lenses and their power, real and virtual images, and ray diagrams with GCSE Bitesize Physics. Lenses are precisely shaped pieces of glass that have been developed and used in corrective glasses, telescopes, microscopes, binoculars, and magnifying glasses.
The Open Door Web Site : IB Physics : OPTICS : RAY DIAGRAMS... Ray Diagrams for Lenses: Examples. A ray diagram can be used to find details of the image formed by a lens (or mirror). It can tell us the size, position and type of image (real or virtual) formed. Two rays are needed to give this information as described here. For simplicity, we usually assume that one end...
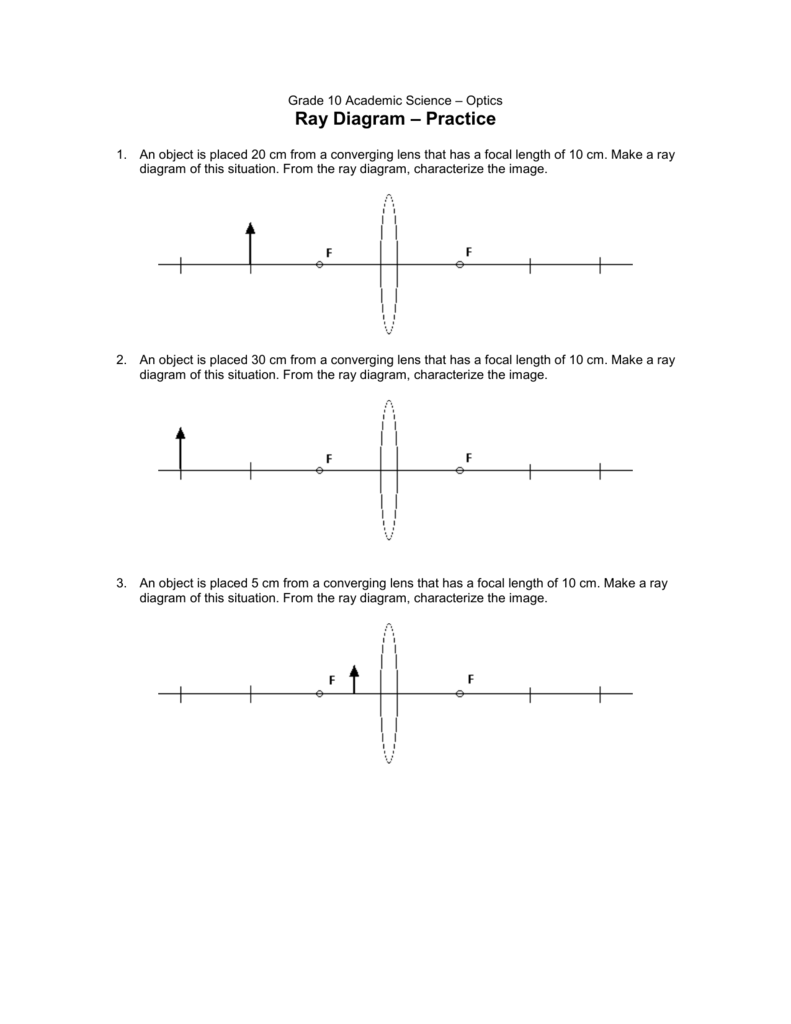
Ray diagram for converging lens
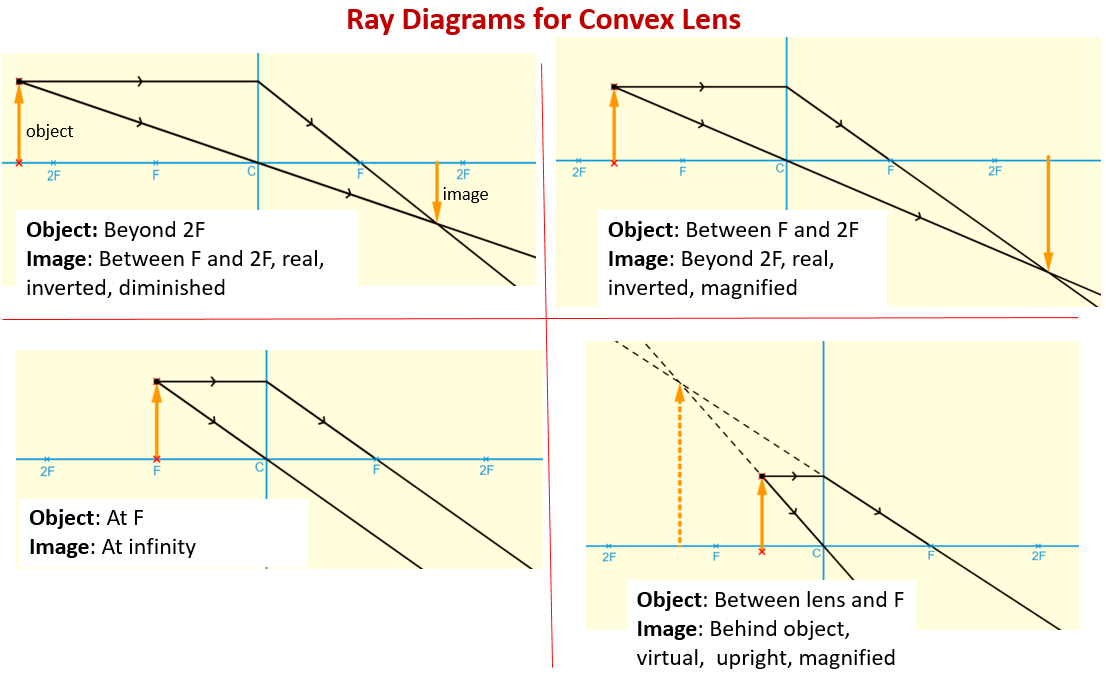
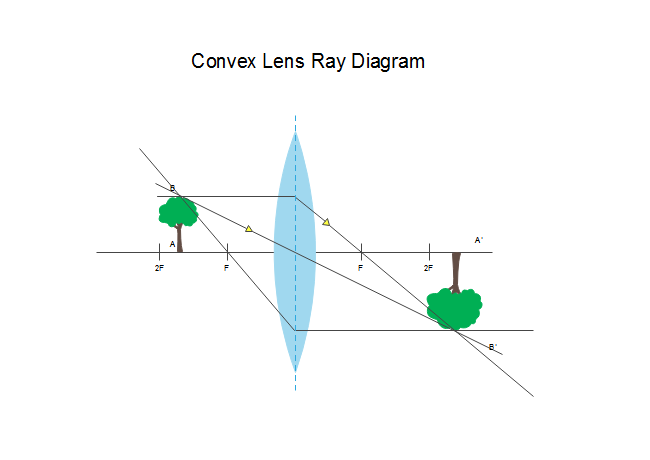
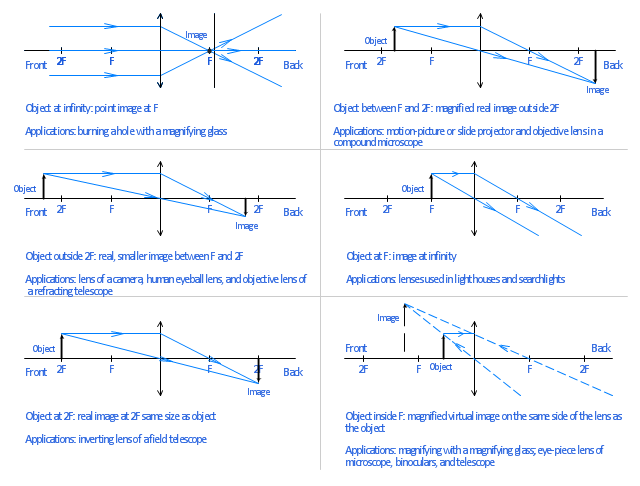
1a A simple ray diagram for a converging convex lens. (d) Convex lens ray diagram for a real image when object is at a distance between F and 2F from lens. the faces of a convex lens curve outwards so it bulges towards it centre, 1a A simple ray diagram for a converging convex lens. For a convex lens, parallel rays are brought to focus at F... hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu › hbase › geooptRay Diagrams for Lenses - Georgia State University Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are: Concave and Convex Mirrors - Ray Diagrams, Image... - GeeksforGeeks As the parallel rays coming from the object converge at the principal focus, F of a concave mirror; after reflection through it. Image Formation By Concave Mirror And Their Ray Diagrams. Two possibilities of the position of the object are possible in the case of a convex mirror, which is when the object at...
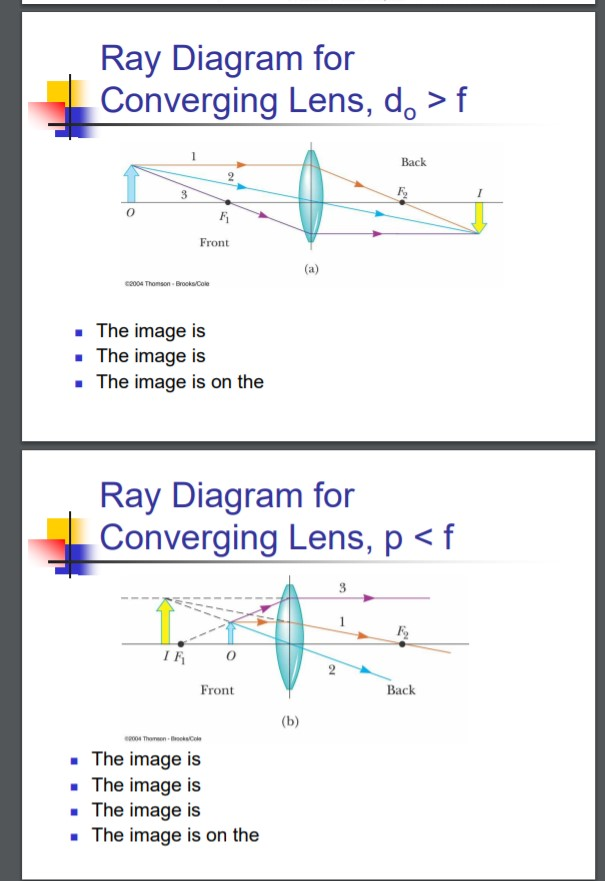
Ray diagram for converging lens. Converging Lens: Definition, Diagram, Equation & Application A converging lens is an optical lens that converges all rays of light passing through it. The primary purpose of a converging lens is to focus the incoming rays from an object and converge them to form an image. Terms Used in Converging Lens Ray Diagram. Ray diagrams for converging lens cases. - SAT II Physics Notes One must look through the lens to see this image. Here are two pictures of actual images produced by converging lenses. Here are ray diagrams for the four cases from the video plus one more when the object is just a little further than the focal point away. PDF Chapter 36 | Ray Diagram for Converging Lens, p < f Lens Refraction Converging & Diverging. Real and Virtual Images. Notation for Mirrors and Lenses. Lateral Magnification. Images Formed by Flat Mirrors. Focal Length Shown by Parallel Rays. Focal Length& Radius of Curvature. Ray Diagrams:Concave Mirrors. Ray Diagram For Converging Lenses Converging (convex) lenses. Ray tracing for thin lenses is very similar to the technique we used with spherical mirrors. As for mirrors, ray tracing can accurately describe the operation of a lens. Ray Diagram For Converging Lenses.
Ray diagrams for converging lenses - YouTube Description of how to draw ray diagrams for converging lenses for grade 10 science. 9.3.2: Lenses and Ray Tracing - Physics LibreTexts Converging Lenses. How could we find the image by the object formed below? For the moment let us just ask about the tip of the arrow. The diagram below shows this conclusion in ray 3 explicitly: Notice that all these rays cross at a particular location. That is where the arrow tip will appear to be to... NUMERICALS BASED ON CONVEX AND CONCAVE LENS - … 10.08.2020 · Q.18. An object 5 cm high is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Find the position, size and nature of the image formed. Also draw the ray diagram. Answer v=16.66 cm, m=-0.66, h=-3.3 cm Ray Diagrams for Lenses - ppt video online download 2 Convex Lens Ray Diagrams All ray diagrams start with a center line and the lens Note: the lens can be simplified into a straight vertical line. 12 A convex (converging) lens can form 3 types of images. The type of image is determined by the object distance. do > 2 f IMAGE = real, inverted...
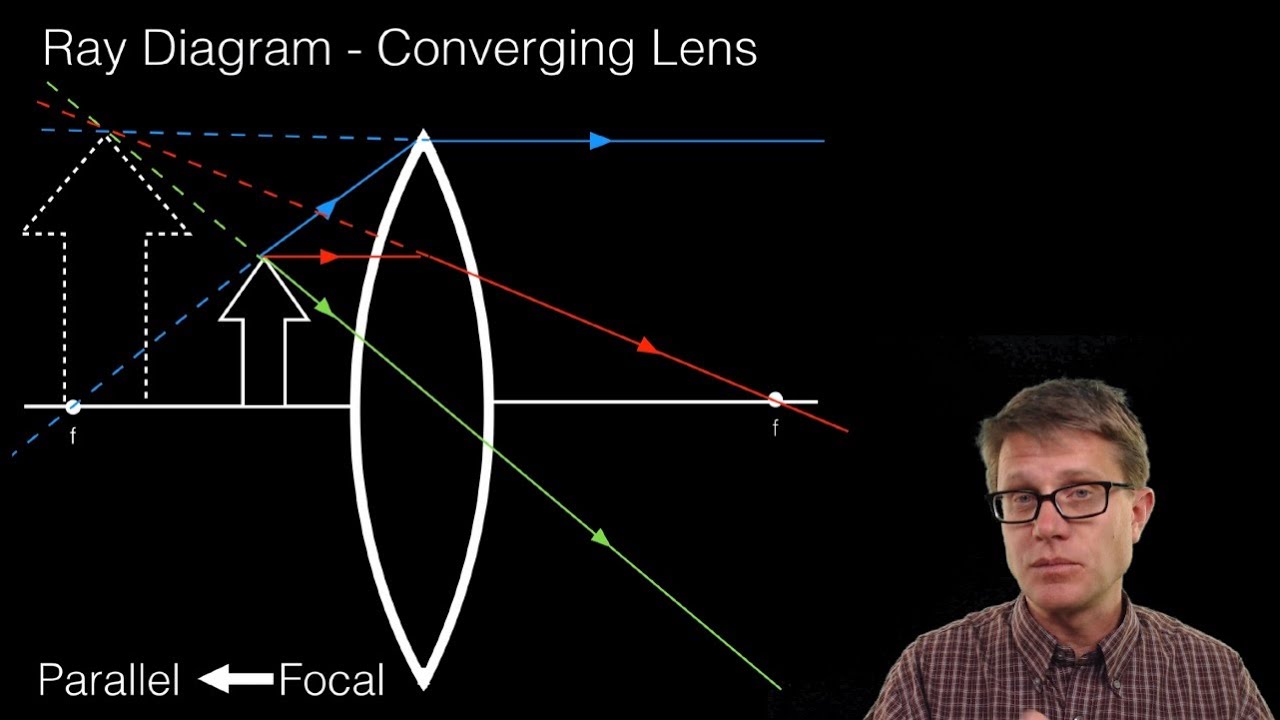
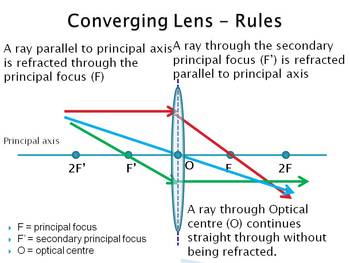
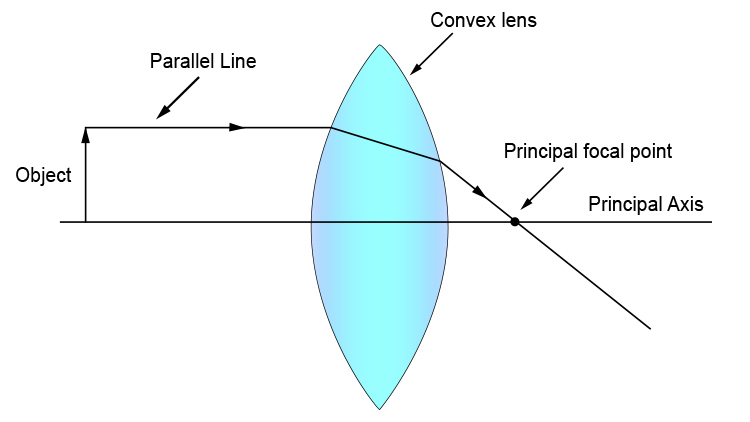
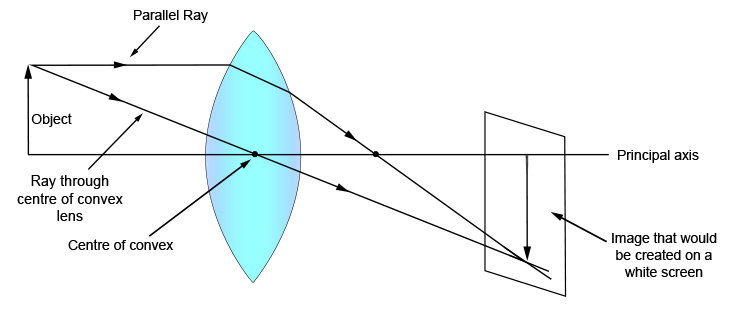
Drawing ray diagrams for a converging lens - The Fizzics Organization To understand how lenses work you often have to draw ray diagrams. To explain how to draw the diagrams, there are two key things to remember. 1 A converging lens refracts the light so that any ray of light parallel to the principal axis (the thick horizontal line) is turned to pass through the focal point. Ray tracing diagram for convex lens | Optics - Vector stencils library "A lens is an optical device which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element. Wikipedia] The example "Ray tracing diagram for convex lens" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software... Converging lens - interactive simulations - eduMedia Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a converging lens. A ray proceeding parallel to the principal axis will pass through the principal focal point beyond the lens, F'. Virtual images are produced when outgoing rays from a single point of the object diverge (never cross). P8.3 - Thin Converging Lens - IGCSE AID A converging lens that is curved on both sides (there are two types of converging lens- concave and convex.) Draw and interpret simple ray diagrams that illustrate the formation of real and virtual images by a single converging lens. Based on where the object is placed, the image formed could...
PDF Converging & Diverging Lenses Ray Diagrams Draw a ray dia Converging & Diverging Lenses Ray Diagrams. Draw a ray diagram for a 5.0-cm tall object placed 45.0 cm from a converging lens having a focal length of 15.0 cm. .
Ray Diagrams for Lenses - Wolfram Demonstrations Project Ray Diagrams for Lenses. Initializing live version. lens type. converging. diverging. focal length. This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses. By manipulating the object and lens locations, you can create real or virtual images.
› class-12-physics-importantRay Optics and Optical Instruments Class 12 Important Extra ... Mar 05, 2021 · An object is placed at a point beyond the focus of lens L 1. Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation by the combination and hence derive the expression for the focal length of the combined system. Answer: Consider two lenses A and B of focal length f 1 and f 2 placed in contact with each other.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a convex lens... Images formed in different lenses. diagram. Characteristics of images by symmetrical lens. > A converging lens of refractive index 1.5 kept in a liquid medium having the same refractive index. What would be the focal length of the lens in this medium?
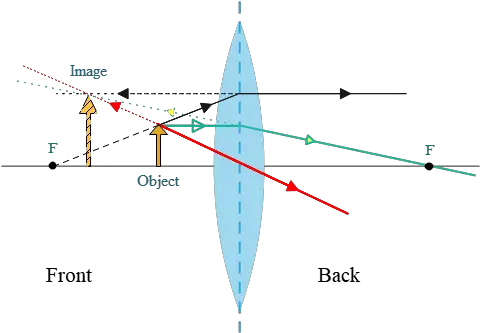
Fig 2. Ray diagram for converging lens: real object, virtual image Ray diagrams for the thin lens. We have already discussed the use of a thin convex lens ( a converging lens) as a magnifying glass. If a small object is placed on the optical axis at a greater distance from the optical centre C than the focal length then the rays from each point on the object...
Image Formation by Lenses | Physics | Converging or Convex Lens The lens in which light rays that enter it parallel to its axis cross one another at a single point on the opposite side with a converging effect is called converging For example, a powerful converging lens will focus parallel light rays closer to itself and will have a smaller focal length than a weak lens.
› class › refrnConverging Lenses - Ray Diagrams - Physics Classroom Image Formation Revisited. Converging Lenses - Ray Diagrams. 2. Once these incident rays strike the lens, refract them according to the three rules of refraction for converging lenses. The ray that passes through the focal point on the way to the lens will refract and travel parallel to the principal axis.
byjus.com › questions › an-object-5-cm-in-length-isAn object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging ... An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed. Given that The height of object = 5cm
Convex Lens - Ray diagram, Image Formation, Table - Teachoo For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positions. Hence, we take different cases. Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity. In this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance). So, we draw rays parallel to principal axis.
Lenses | Ray diagram for a diverging lens Consider now the ray diagram for a diverging lens. Note that a diverging lens will refract parallel rays so that they diverge from each other, while a converging lens refracts parallel rays toward each other.
SS: Ray Diagrams For Converging Lens - Mini Physics - Learn Physics Thin converging lenses. Ray diagrams for converging lens. If a ray is parallel to principal axis before passing through the lens, the refracted ray will pass through the focal point. Tips: Use solid lines for real light rays and put arrowheads to indicate direction.
Concave Lens Ray Diagrams Convex & Concave Ray Diagrams. Lenses can be used to form images of objects placed in front of them. The location (and nature) If an object is placed further from the lens than the focal length f then a real image will be formed, and the converging lens ray diagram will be drawn in the following way
Ray Tracing for Converging Lenses Get started drawing a ray diagram for converging lens, by drawing an optical axis. Now, put your lens on this axis somewhere, kind of in the middle to give yourself some room to work. Draw the center of the lens first, using your protractor to make sure it is perpendicular to your optical axis and that all...
› 10839 › 3118Concave Lens - Ray diagram, Images Formed - teachoo Apr 26, 2020 · For a Concave lens,There are only 2 casesThey areObject is Placed at InfinityObject is Placed between Infinity and Optical CenterCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray pa
› 10842 › 3118Lens Formula - and Magnification Formula - with Numericals ... Apr 26, 2020 · NCERT Question 10 - An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed View Answer NCERT Question 11 - A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10 cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the lens?
PhysicsLAB: Converging Lenses | Ray #3 (pink) Any lens that is "thicker in the center" than on the edges is generally described as a convex lens and will This position is located behind the lens and is usually labeled as F in ray diagrams. Whenever the actual rays of light that refract through the lens converge behind the lens to form an image, that...
PDF Lenses | Ray Diagrams Converging Lenses · Ray 1 - _ to principal _, bends 6. How far from the lens must the film in a camera be, if the lens has a 35.0 mm focal length and is being used to photograph a flower 75.0 cm away? Solve using both a ray diagram and the thin lens equation.
physics.fullerton.edu › files › LabsReflection and Refraction - California State University ... G) Turn over the ray box and slide the mask so that only red light is emerging. (You can use the diverging lens on its side to prop up the edge of the Ray Box to lengthen the light ray. See Figure 11 later in the lab.) Overlay the red light ray on top of the incident ray that you already drew. YOU DON’T HAVE TO TRACE IT. Observe how the ray ...
Concave and Convex Mirrors - Ray Diagrams, Image... - GeeksforGeeks As the parallel rays coming from the object converge at the principal focus, F of a concave mirror; after reflection through it. Image Formation By Concave Mirror And Their Ray Diagrams. Two possibilities of the position of the object are possible in the case of a convex mirror, which is when the object at...
hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu › hbase › geooptRay Diagrams for Lenses - Georgia State University Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are:
1a A simple ray diagram for a converging convex lens. (d) Convex lens ray diagram for a real image when object is at a distance between F and 2F from lens. the faces of a convex lens curve outwards so it bulges towards it centre, 1a A simple ray diagram for a converging convex lens. For a convex lens, parallel rays are brought to focus at F...
























Comments
Post a Comment